A dialyzer, commonly known as an artificial kidney, is a crucial medical device used in hemodialysis to remove waste products and excess fluids from the blood of patients with kidney failure. It plays a central role in the dialysis process, effectively replacing the filtering function of the kidneys. Understanding how a dialyzer works and its various components is essential for both healthcare professionals and patients.
Dialyzer Function in Hemodialysis
The primary dialyzer function is to filter toxins, electrolytes, and excess fluids from the bloodstream. During hemodialysis, blood is drawn from the patient and passed through the dialyzer. Inside, it flows along one side of a semi-permeable membrane, while a special dialysis fluid (dialysate) flows on the opposite side. This setup allows waste and excess substances to pass from the blood into the dialysate, while retaining essential components like blood cells and proteins.
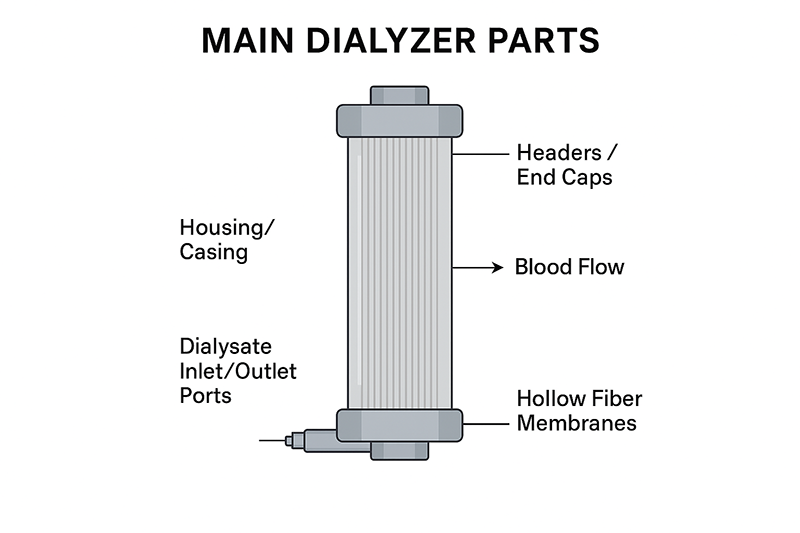
Main Dialyzer Parts
Understanding the dialyzer parts helps in comprehending how efficiently it operates. A typical dialyzer consists of the following components:
- Housing/Casing – A plastic cylindrical shell that encloses the inner components.
- Hollow Fiber Membranes – Thousands of thin fibers made of semi-permeable material through which blood flows.
- Headers and End Caps – Secure the fibers and control blood flow in and out of the dialyzer.
- Dialysate Inlet/Outlet Ports – Allow the dialysate to circulate around the fibers.
The Role of the Dialyzer Filter
The dialyzer filter is the semi-permeable membrane inside the dialyzer. It is the core component that facilitates the exchange of substances between the blood and the dialysate. Its microscopic pores are small enough to allow urea, creatinine, potassium, and excess fluids to pass through, while preventing the loss of vital blood components like red blood cells and proteins. The quality and pore size of the filter membrane directly affect the efficiency of dialysis.
Different Dialyzer Types
There are several dialyzer types available, and the choice depends on the patient’s condition, dialysis prescription, and treatment goals:
- Low-Flux Dialyzers – Have smaller pores, allowing limited removal of molecules; suitable for standard hemodialysis.
- High-Flux Dialyzers – Have larger pores for better clearance of middle molecules; commonly used in modern dialysis for enhanced toxin removal.
- High-Efficiency Dialyzers – Designed with larger surface areas to filter blood quickly; used in high-efficiency dialysis sessions.
- Single-Use vs. Reusable Dialyzers – Depending on clinical protocols and cost, some dialyzers are discarded after one use, while others are sterilized and reused.
Choosing the Right Dialyzer Size
Dialyzer size refers mainly to the surface area of the filter membrane and the internal volume that can handle blood flow. A larger surface area means a greater capacity to remove waste, making it suitable for adult patients with higher body weight. Pediatric patients or those with low blood volume may require smaller dialyzers. Choosing the right size ensures optimal clearance and patient safety.
Conclusion: Why the Dialyzer Matters
The dialyzer is the heart of the hemodialysis system, replacing essential kidney functions for patients with renal failure. By understanding the different dialyzer types, dialyzer parts, dialyzer filter capabilities, and appropriate dialyzer size, healthcare providers can optimize treatment plans and improve patient outcomes. With advancements in membrane technology and device design, dialyzers continue to evolve, offering better efficiency and comfort for dialysis patients worldwide.
Post time: Aug-19-2025