1. Understanding Different Types of Syringes
Syringes come in various types, each designed for specific medical tasks. Choosing the right syringe begins with understanding its intended purpose.
2. What Is Hypodermic Needle Gauge?
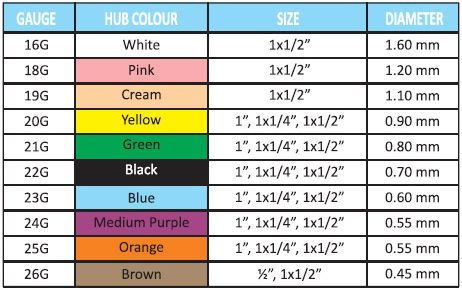
The needle gauge refers to the diameter of the needle. It’s denoted by a number—commonly ranging from 18G to 30G, where higher numbers indicate thinner needles.
| Gauge | Outer Diameter (mm) | Common Use |
|---|---|---|
| 18G | 1.2 mm | Blood donation, thick medications |
| 21G | 0.8 mm | General injections, drawing blood |
| 25G | 0.5 mm | Intradermal, subcutaneous injections |
| 30G | 0.3 mm | Insulin, pediatric injections |
Needle gauze size chart
3. How to Choose the Right Needle Gauge
Choosing the right needle gauge and length depends on multiple factors:
- Viscosity of the medication: Thick liquids need larger bore needles (18G–21G).
- Injection route:Patient type: Use smaller gauges for children and elderly patients.
- Intramuscular (IM): 22G–25G, 1 to 1.5 inch
- Subcutaneous (SC): 25G–30G, ⅜ to ⅝ inch
- Intradermal (ID): 26G–30G, ⅜ to ½ inch
- Pain sensitivity: Higher gauge (thinner) needles reduce injection discomfort.
Pro tip: Always follow clinical standards when selecting needles and syringes.
4. Matching Syringes and Needles to Medical Applications
Use the chart below to determine the right combination of syringe and needle based on your application:
| Application | Syringe Type | Needle Gauge & Length |
|---|---|---|
| Intramuscular injection | Luer Lock, 3–5 mL | 22G–25G, 1–1.5 inch |
| Subcutaneous injection | Insulin syringe | 28G–30G, ½ inch |
| Drawing blood | Luer Lock, 5–10 mL | 21G–23G, 1–1.5 inch |
| Pediatric medication | Oral or 1 mL TB syringe | 25G–27G, ⅝ inch |
| Wound irrigation | Luer Slip, 10–20 mL | No needle or 18G blunt tip |
5. Tips for Medical Suppliers and Bulk Buyers
If you are a distributor or medical procurement officer, consider the following when sourcing syringes in bulk:
- Regulatory compliance: FDA/CE/ISO certification required.
- Sterility: Choose individually packed syringes to avoid contamination.
- Compatibility: Ensure syringe and needle brands match or are universally compatible.
- Shelf life: Always confirm expiration dates before mass purchase.
Reliable suppliers help reduce costs and ensure consistent product quality for healthcare providers.
Post time: Jul-01-2025