In the field of medical consumables, selecting the right needle is critical for patient comfort, clinical efficiency, and cost control. Among the most commonly used blood collection devices, butterfly needles and straight needles are widely applied in hospitals, clinics, laboratories, and blood banks.
This article provides a clear comparison of butterfly needle vs straight needle, helping healthcare professionals, distributors, and medical supply buyers understand their structures, benefits, disadvantages, and ideal applications.
What Is a Butterfly Needle?
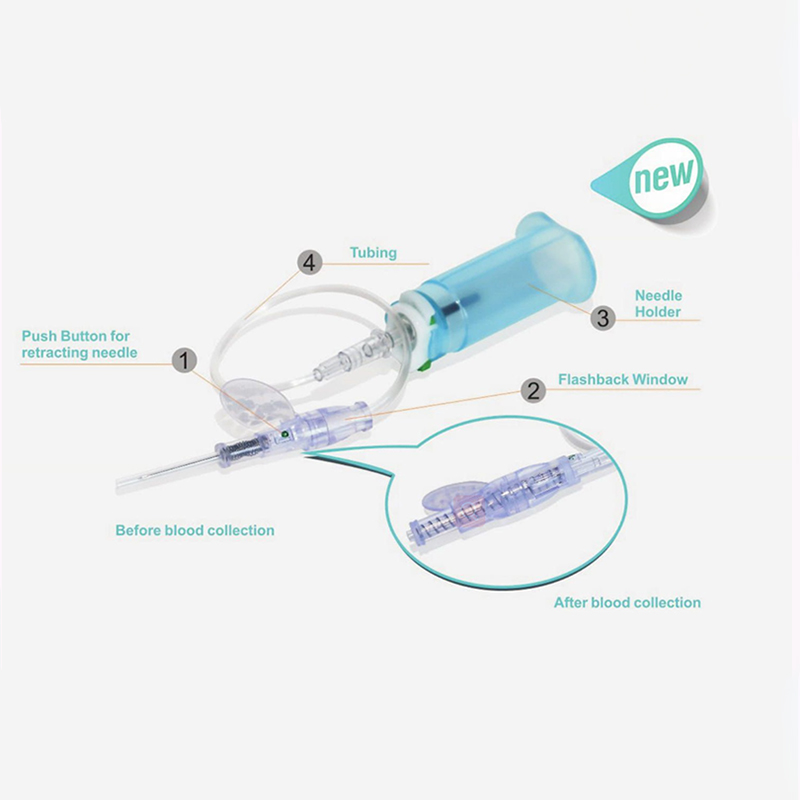
A butterfly needle, also known as a winged infusion set, is a small-bore needle commonly used for venipuncture and blood collection, especially in patients with fragile or difficult-to-access veins.
Structure and Functions of a Butterfly Needle
A typical butterfly needle consists of:
A short, thin needle (usually 21G–25G)
Two flexible plastic wings on each side
Transparent flexible tubing
A connector (luer adapter or holder)
The wings allow healthcare professionals to stabilize the needle during insertion, while the flexible tubing reduces movement at the puncture site. As a medical device, butterfly needles are designed to improve precision and patient comfort during blood collection.
Benefits of Butterfly Needle
Butterfly needles are widely used in pediatric care, geriatrics, and oncology due to several advantages:
1. Improved Patient Comfort
Smaller gauge needles cause less pain, making them suitable for sensitive patients.
2. Better Control and Accuracy
The winged design offers greater stability during insertion, reducing the risk of vein damage.
3. Ideal for Difficult Veins
Butterfly needles work well for small, fragile, or rolling veins.
4. Reduced Risk of Needle Movement
Flexible tubing minimizes needle displacement during blood collection.
These features make butterfly needles a preferred blood collection device in many clinical settings.
Disadvantages of Butterfly Needle
Despite their advantages, butterfly needles also have limitations:
Higher Cost compared to straight needles
Slower Blood Flow due to smaller needle gauge
Not Ideal for Large-Volume Blood Collection
Higher Hemolysis Risk if improper technique is used
From a medical supply procurement perspective, cost and efficiency must be considered when choosing butterfly needles.
What Is a Straight Needle?
A straight needle is a traditional venipuncture needle commonly used with vacuum blood collection tubes or syringes. It is one of the most widely used medical consumables in hospitals and laboratories.
Structure and Functions of a Straight Needle
A straight needle typically includes:
A single straight stainless-steel needle
A plastic hub
Compatibility with vacuum tube holders or syringes
Straight needles are designed for direct, efficient blood flow and are commonly used for routine blood draws.
Benefits of Straight Needle
Straight needles remain popular due to their practicality and efficiency:
1. Faster Blood Collection
Larger gauges allow higher blood flow rates.
2. Cost-Effective
Straight needles are generally cheaper, ideal for high-volume use.
3. Suitable for Routine Venipuncture
Effective for patients with healthy, visible veins.
4. Wide Availability
Easily sourced as standard medical consumables worldwide.
For distributors and wholesalers, straight needles are a staple medical supply with consistent demand.
Disadvantages of Straight Needle
However, straight needles are not suitable for all situations:
Less Control During Insertion
Higher Risk of Vein Damage in fragile veins
More Pain for Sensitive Patients
Not Ideal for Pediatric or Geriatric Use
Proper patient assessment is essential when selecting this blood collection device.
Differences Between Butterfly Needles and Straight Needles
| Feature | Butterfly Needle | Straight Needle |
| Design | Winged with flexible tubing | Straight, rigid needle |
| Patient Comfort | High | Moderate |
| Blood Flow Speed | Slower | Faster |
| Best for | Small, fragile, or hard-to-access veins | Large, visible veins |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Common Use | Home draws, pediatrics, geriatrics | Hospitals, labs, urgent care |
| Stability | Excellent control | Requires steady hand |
This table clearly highlights the key differences between butterfly needles and straight needles for quick reference.
How to Choose the Right Needle for You?
Choosing between a butterfly needle vs straight needle depends on several factors:
Patient Type: Pediatric, elderly, or difficult veins favor butterfly needles
Procedure Type: Routine blood draws may benefit from straight needles
Blood Volume Required: Large-volume collection suits straight needles
Cost Considerations: High-volume facilities often prefer straight needles
Clinical Environment: Emergency vs outpatient settings
For medical supply buyers and distributors, balancing performance, cost, and application is essential when selecting the right medical device.
Final Thoughts
Both butterfly needles and straight needles play essential roles in modern healthcare. As critical blood collection devices, they serve different clinical needs and patient populations. Understanding their differences helps healthcare providers, procurement teams, and medical consumables suppliers make informed decisions.
If you are sourcing medical supplies or exporting medical consumables, selecting the right needle type can improve efficiency, patient satisfaction, and overall clinical outcomes.
Post time: Jan-26-2026